We actively develop Netdata to add new features and remove bugs, and encourage all users to ensure they're using the most up-to-date version, whether that's nightly or major releases.
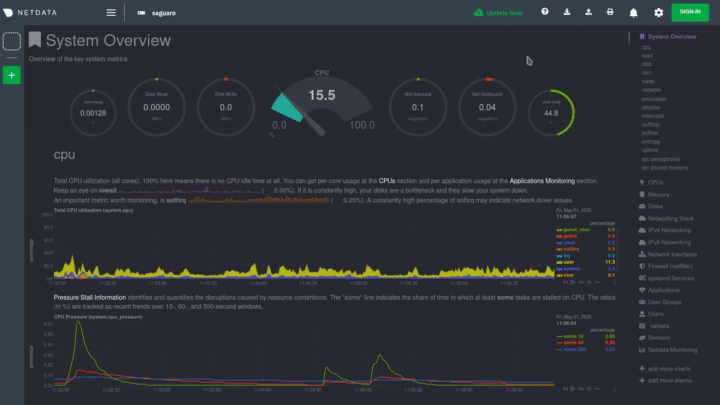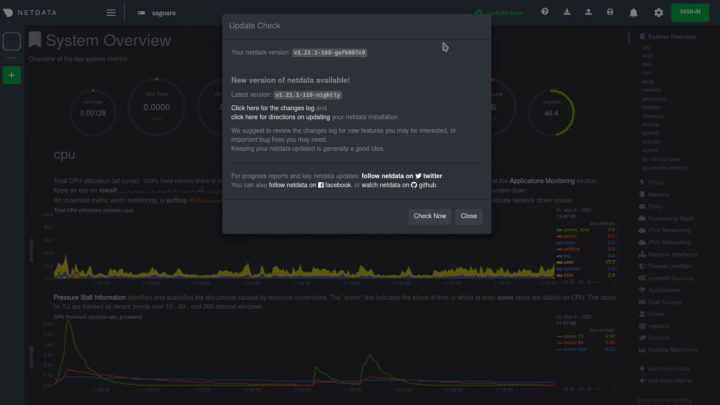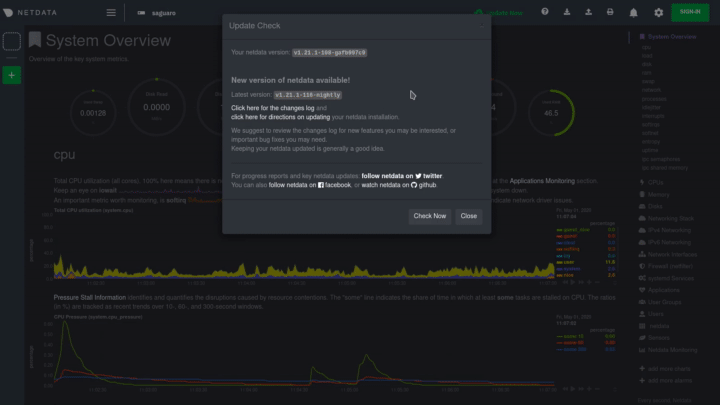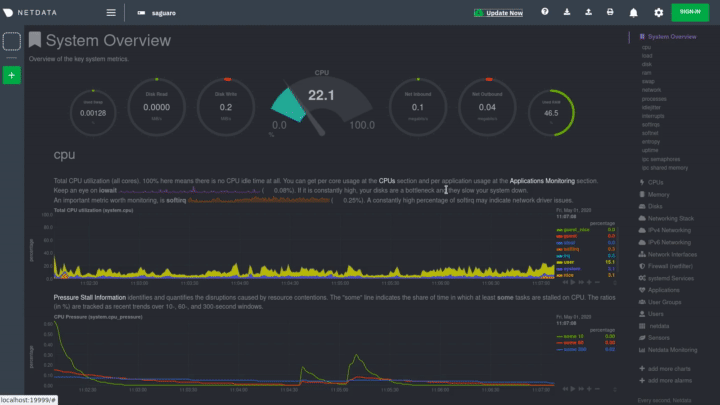
Before you update Netdata using one of the methods below, check to see if your Netdata agent is already up-to-date by opening the update modal in the dashboard. Click the Update button in the top navigation to open it. The modal tells you whether your agent is up-to-date or not.
If your agent can be updated, use one of the methods below. The method you chose for updating Netdata depends on how you installed it. Choose from the following list to see the appropriate update instructions for your system.
- One-line installer script (
kickstart.sh) .debor.rpmpackages- Pre-built static binary for 64-bit systems (
kickstart-static64.sh) - Docker
- macOS
- Manual installation from Git
First, see here to figure out where your user configuration files for Netdata are.
Once you have figured this out, look for a file called .environment in this directory (you will need to use
ls -a to see it, as it will not be listed by default by a regular ls command). If it is not there, you used
package manager to install netdata and need to update it through that package manager. If the environment file
is present, check the contents of the file. If IS_NETDATA_STATIC_BINARY is "yes", then you installed using
kickstart-static64.sh. Otherwise you installed using kickstart.sh.
If you installed Netdata using our one-line automatic installation script, run it again to update Netdata. Any custom
settings present in your Netdata configuration directory (typically at /etc/netdata) persists during this process.
This script will automatically run the update script that was installed as part of the initial install (even if you disabled automatic updates) and preserve the existing install options you specified.
If you installed Netdata using an installation prefix, you will need to add an --install option specifying
that prefix to this command to make sure it finds Netdata.
bash <(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh)In the event that this command fails, there may be an issue with the installed update script. In such cases, you can instead use the following command to run an update as if it were a clean install (this will still preserve any user configuration).
bash <(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh) --reinstallIf using this method, you will need to pass any options you passed during the original installation process. To
determine what options you passed, start by finding the .environment file for your install as described above in
How to determine which install method you used. Once you have
found this file, look at the value of the REINSTALL_OPTIONS line. This is the list of additional options you
need to pass to the above command.
If you installed Netdata with .deb or .rpm packages, use your distribution's package manager update Netdata. Any
custom settings present in your Netdata configuration directory (typically at /etc/netdata) persists during this
process.
Your package manager grabs a new package from our hosted repository, updates Netdata, and restarts it.
apt-get install netdata # Ubuntu/Debian
dnf install netdata # Fedora/RHEL
yum install netdata # CentOS
zypper in netdata # openSUSEYou may need to escalate privileges using
sudo.
If you installed Netdata using the pre-built static binary, run the kickstart-static64.sh script again to update
Netdata. Any custom settings present in your Netdata configuration directory (typically at /etc/netdata) persists
during this process.
This script will automatically run the update script that was installed as part of the initial install (even if you disabled automatic updates) and preserve the existing install options you specified.
bash <(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart-static64.sh)In the event that this command fails, there may be an issue with the installed update script. In such cases, you can instead use the following command to run an update as if it were a clean install (this will still preserve any user configuration).
bash <(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart-static64.sh) --reinstallIf using this method, you will need to pass any options you passed during the original installation process. To
determine what options you passed, start by finding the .environment file for your install as described above in
How to determine which install method you used. Once you have
found this file, look at the value of the REINSTALL_OPTIONS line. This is the list of additional options you
need to pass to the above command.
Docker-based installations do not update automatically. To update an agent running in a Docker container, you must pull the latest image from Docker hub, stop and remove the container, and re-create it using the latest image.
First, pull the latest version of the image.
docker pull netdata/netdata:latestNext, to stop and remove any containers using the netdata/netdata image. Replace netdata if you changed it from the
default in our Docker installation
instructions.
docker stop netdata
docker rm netdataYou can now re-create your Netdata container using the docker command or a docker-compose.yml file. See our Docker
installation instructions for details. For
example, using the docker command:
docker run -d --name=netdata \
-p 19999:19999 \
-v /etc/passwd:/host/etc/passwd:ro \
-v /etc/group:/host/etc/group:ro \
-v /proc:/host/proc:ro \
-v /sys:/host/sys:ro \
-v /etc/os-release:/host/etc/os-release:ro \
--cap-add SYS_PTRACE \
--security-opt apparmor=unconfined \
netdata/netdataIf you installed Netdata on your macOS system using Homebrew, you can explictly request an update:
brew upgrade netdataHomebrew downloads the latest Netdata via the formulae, ensures all dependencies are met, and updates Netdata via reinstallation.
If you installed Netdata manually from Git using netdata-installer.sh, you can run that installer again to update your
agent. First, run our automatic requirements installer, which works on many Linux distributions, to ensure your system
has the dependencies necessary for new features.
bash <(curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/netdata/netdata/master/packaging/installer/install-required-packages.sh)Then, navigate to the directory where you first cloned the Netdata repository, pull the latest source code, and run
netdata-install.sh again. This process compiles Netdata with the latest source code and updates it via reinstallation.
cd /path/to/netdata/git
git pull origin master
sudo ./netdata-installer.sh
⚠️ If you installed Netdata with any optional parameters, such as--no-updatesto disable automatic updates, and want to retain those settings, you need to set them again during this process.