https://github.com/flatironinstitute/learn-sciware-dev/tree/master/15_IntroGithub
Activities where participants all actively work to foster an environment which encourages participation across experience levels, coding language fluency, technology choices*, and scientific disciplines.
*though sometimes we try to expand your options
- Avoid discussions between a few people on a narrow topic
- Provide time for people who haven't spoken to speak/ask questions
- Provide time for experts to share wisdom and discuss
- Work together to make discussions accessible to novices
- If comfortable, please keep video on so we can all see each other's faces.
- Ok to break in for quick, clarifying questions.
- Use Raise Hand feature for new topics or for more in-depth questions.
- Please stay muted if not speaking. (Host may mute you.)
- We are recording. Link will be posted on #sciware Slack.
- Tomorrow: Github Part 2: collaboration
- July 8: Intro to IDEs and Debugging
- Suggest topics and vote on options in #sciware Slack
- What is Git and GitHub?
- Setting up git and GitHub on your computer
- Getting code off of GitHub
- Putting code onto GitHub
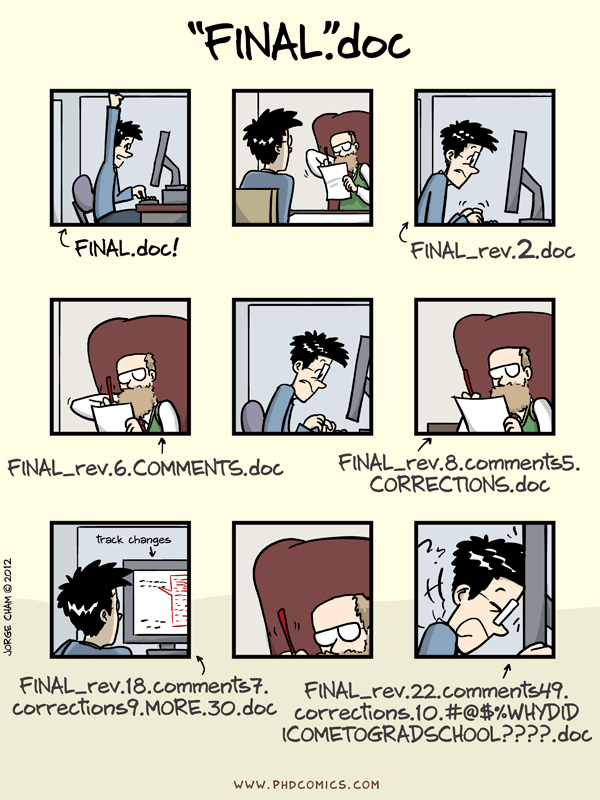
- keeps track of history of one or more files
- helps with backup and collaboration
- makes it easier to combine changes to the same file
an open-source, distributed, command-line, version-control tool
- released in 2005 by Linus Torvalds for developing Linux, as an alternative to older tools (CVS, svn)
- now the dominant tool for academic and industry software development
- distributed: no central server, every repo is fully functional, independent, and can "sync" with any other
- A central website for storing and sharing git repositories
- Started in 2008 as a freemium service, now owned by Microsoft
- Provides repository management, permissions, collaboration tools, CI, etc.
> git version
git version 2.30.1
If this returns an error, please raise your hand and someone can help you in a breakout room.
See what name is currently set
> git config --global user.name
Set your name
> git config --global user.name "Mona Lisa"
> git config --global user.email
> git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
(Ideally set to the same email address you used for Github.)
> ssh-keygen -t ed25519
> cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
It is easiest to leave the password blank.
- On Github:
- Profile Photo > Settings > SSH and GPG keys > New SSH Key
-
Title should refer to the computer on which the key was generated.
-
Paste key into text box.
- So that you don't get stuck in vi:
> git config --global core.editor "nano -w"
- How to set up your favorite editor with Git:
https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Appendix-C%3A-Git-Commands-Setup-and-Config#ch_core_editor

- Folder containing the code - repository or repo, for short
- "Download the code" - clone the repo
- Your computer harddrive - local
Download the code to your computer in GitHub-ese is
Clone the Repo to your local

- Go to the repo on the Github website
- Click Green Code button
- Choose SSH tab
- Click the clipboard icon to copy the repo path
- In a Terminal window, clone the repo:
> git clone [email protected]:flatironinstitute/sciware15-git-intro
> cd sciware15-git-intro
A folder will be created containing all of the files in the repo.
The folder name will be the repo name.
Using the git clone command connects the folder to the repo on GitHub in case you ever wanted to interact with it later.
- It generates hidden folder
.git
> ls -a
- It also saves the URL to the repo and names it origin
> git remote -v
origin [email protected]:flatironinstitute/sciware15-git-intro (fetch)
origin [email protected]:flatironinstitute/sciware15-git-intro (push)
> mkdir silly_project
> cd silly_repo
> touch silly_code.py
> touch silly_funct.py

- Go to your homepage on Github
- Click the Repositories tab
- Click the green New button
- Name the repository silly_repo
> git init
> git status
It's possible to have multiple branches of the code where different things are being worked on.
The primary branch is usually called main.
> git branch -M main
> git status
Notice:
- branch name
silly_file.txtis in red and is untracked
Use the git add command to specify exactly which files you want to transfer to Github.
> git status
> git add silly_file.txt
> git status
Notice:
silly_file.txtis now greensilly_file.txtneeds to be committed
Use the git commit to save the local changes.
Add a commit message to document the changes.
Launch a text editor where you can type the commit message:
> git commit
Alternatively, you can commit directly from the command line:
> git commit -m "add silly file"
> git status
Use git remote add to provide the URL to the Github repo.
The repo that is in your personal profile is usually called origin
> git remote -v
> git remote add origin [email protected]:kelle/silly_project.git
> git remote -v
Use the git push command to upload the committed changes to the Github repo.
> git push origin main
silly_file.txt should now be in the repo on the Github website.
- Find Github buddies
- The best way to figure things out is by asking folks for help
- Avoid problems by keeping track of the state of your local.
- Inspect
git statusbefore and after every command until you gain confidence
- There are many resources for common git and Github problems on the internet.
- Consider discussing with a buddy before copy/pasting.









