🤗 transformers is a library maintained by Hugging Face and the community, for state-of-the-art Machine Learning for Pytorch, TensorFlow and JAX. It provides thousands of pretrained models to perform tasks on different modalities such as text, vision, and audio. We are a bit biased, but we really like 🤗 transformers!
There are over 25,000 transformers models in the Hub which you can find by filtering at the left of the models page.
You can find models for many different tasks:
- Extracting the answer from a context (question-answering).
- Creating summaries from a large text (summarization).
- Classify text (e.g. as spam or not spam, text-classification).
- Generate a new text with models such as GPT (text-generation).
- Identify parts of speech (verb, subject, etc.) or entities (country, organization, etc.) in a sentence (token-classification).
- Transcribe audio files to text (automatic-speech-recognition).
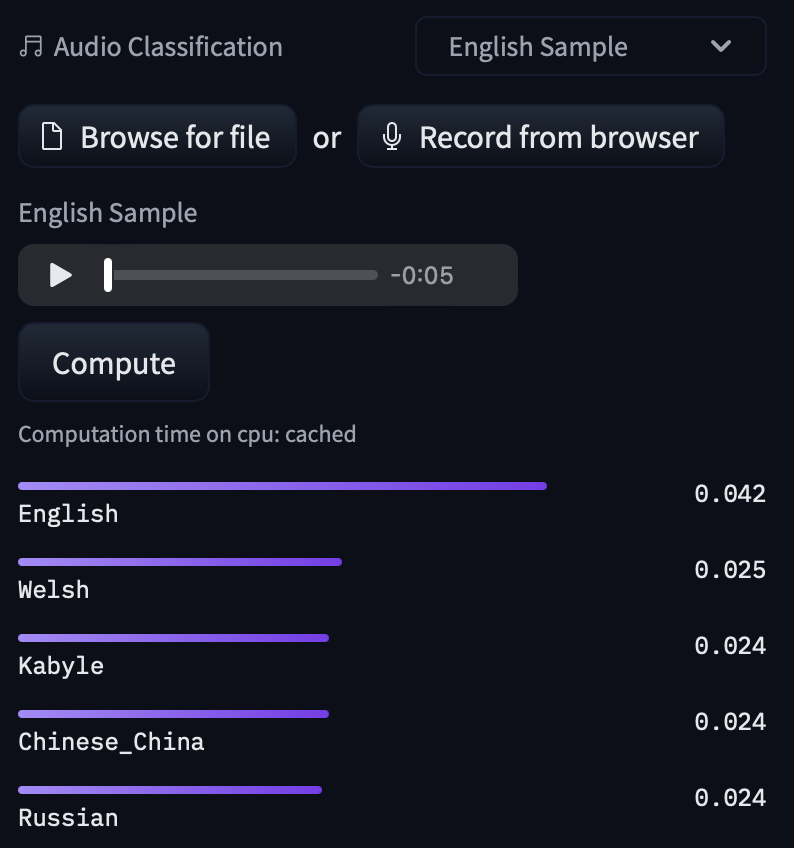
- Classify the speaker or language in an audio file (audio-classification).
- Detect objects in an image (object-detection).
- Segment an image (image-segmentation).
- Do Reinforcement Learning (reinforcement-learning)!
You can try out the models directly in the browser if you want to test them out without downloading them thanks to the in-browser widgets!
A Transformers model repository generally contains model files and preprocessor files.
-
The
config.jsonfile stores details about the model architecture such as the number of hidden layers, vocabulary size, number of attention heads, the dimensions of each head, and more. This metadata is the model blueprint. -
The
model.safetensorsfile stores the models pretrained layers and weights. For large models, the safetensors file is sharded to limit the amount of memory required to load it. Browse themodel.safetensors.index.jsonfile to see which safetensors file the model weights are being loaded from.{ "metadata": { "total_size": 16060522496 }, "weight_map": { "lm_head.weight": "model-00004-of-00004.safetensors", "model.embed_tokens.weight": "model-00001-of-00004.safetensors", ... } }You can also visualize this mapping by clicking on the ↗ button on the model card.
Safetensors is a safer and faster serialization format - compared to pickle - for storing model weights. You may encounter weights pickled in formats such as
bin,pth, orckpt, butsafetensorsis increasingly adopted in the model ecosystem as a better alternative. -
A model may also have a
generation_config.jsonfile which stores details about how to generate text, such as whether to sample, the top tokens to sample from, the temperature, and the special tokens for starting and stopping generation.
- The
tokenizer_config.jsonfile stores the special tokens added by a model. These special tokens signal many things to a model such as the beginning of a sentence, specific formatting for chat templates, or indicating an image. This file also shows the maximum input sequence length the model can accept, the preprocessor class, and the outputs it returns. - The
tokenizer.jsonfile stores the model's learned vocabulary. - The
special_tokens_map.jsonis a mapping of the special tokens. For example, in Llama 3.1-8B-Instruct, the beginning of string token is"<|begin_of_text|>".
Tip
For other modalities, the tokenizer_config.json file is replaced by preprocessor_config.json.
All transformer models are a line away from being used! Depending on how you want to use them, you can use the high-level API using the pipeline function or you can use AutoModel for more control.
# With pipeline, just specify the task and the model id from the Hub.
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", model="distilbert/distilgpt2")
# If you want more control, you will need to define the tokenizer and model.
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilgpt2")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilgpt2")You can also load a model from a specific version (based on commit hash, tag name, or branch) as follows:
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
"julien-c/EsperBERTo-small", revision="v2.0.1" # tag name, or branch name, or commit hash
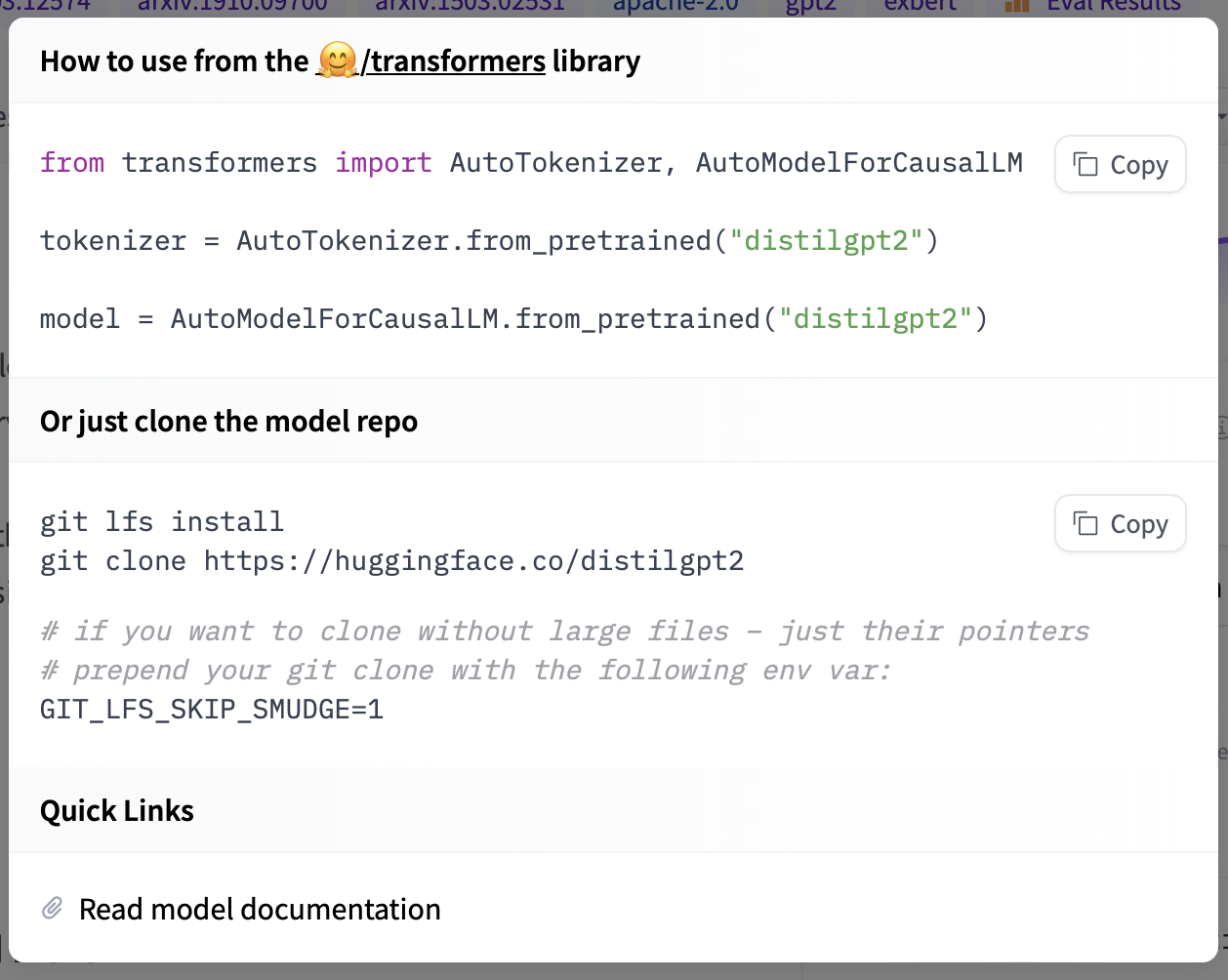
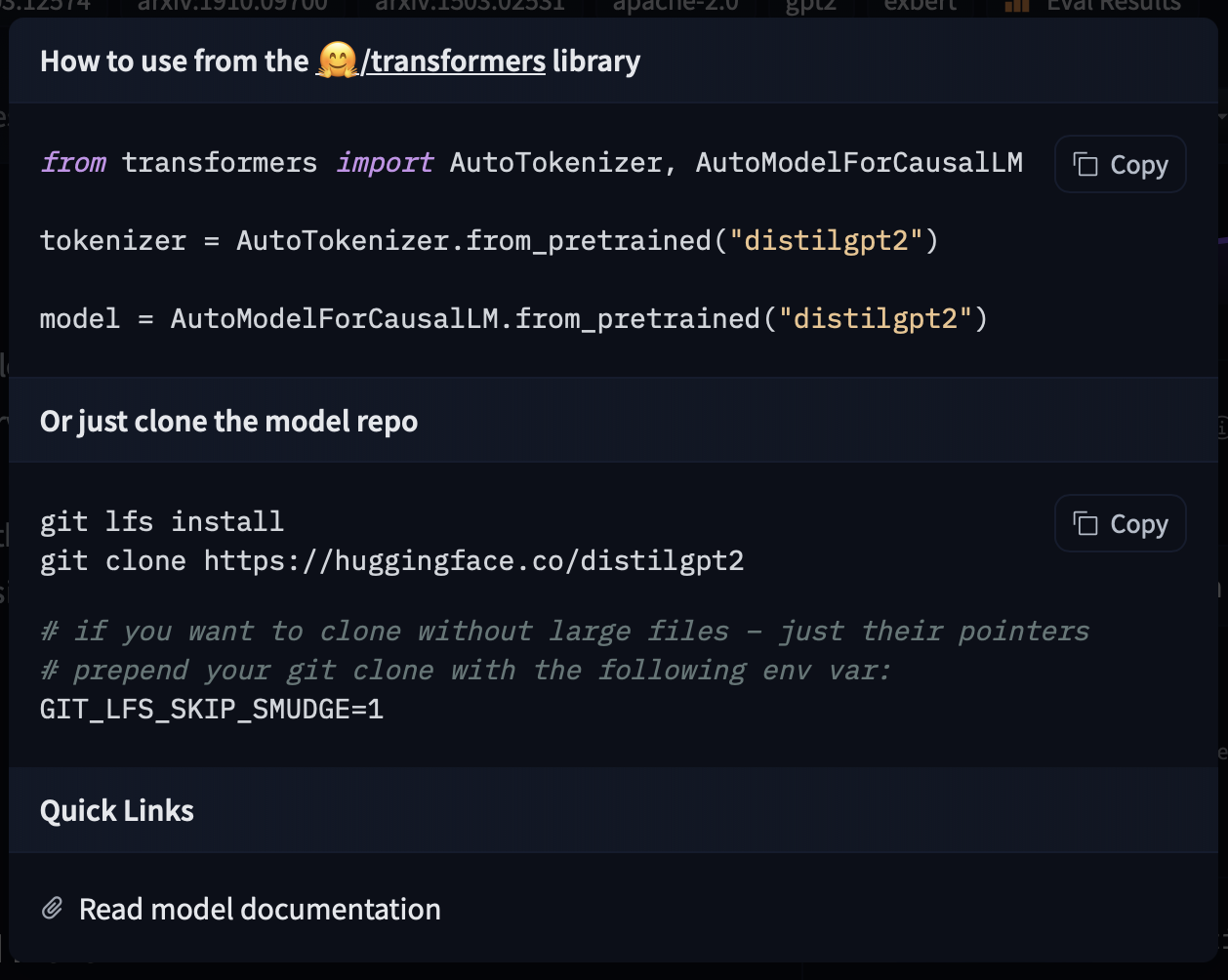
)If you want to see how to load a specific model, you can click Use in Transformers and you will be given a working snippet that you can load it! If you need further information about the model architecture, you can also click the "Read model documentation" at the bottom of the snippet.
To read all about sharing models with transformers, please head out to the Share a model guide in the official documentation.
Many classes in transformers, such as the models and tokenizers, have a push_to_hub method that allows to easily upload the files to a repository.
# Pushing model to your own account
model.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
# Pushing your tokenizer
tokenizer.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
# Pushing all things after training
trainer.push_to_hub()There is much more you can do, so we suggest to review the Share a model guide.