diff --git a/src/main/java/g1601_1700/s1616_split_two_strings_to_make_palindrome/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g1601_1700/s1616_split_two_strings_to_make_palindrome/Solution.java
index f45860a9e..95a950eac 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g1601_1700/s1616_split_two_strings_to_make_palindrome/Solution.java
+++ b/src/main/java/g1601_1700/s1616_split_two_strings_to_make_palindrome/Solution.java
@@ -1,28 +1,32 @@
package g1601_1700.s1616_split_two_strings_to_make_palindrome;
-// #Medium #String #Greedy #Two_Pointers #2022_04_13_Time_4_ms_(89.77%)_Space_43.3_MB_(85.58%)
+// #Medium #String #Greedy #Two_Pointers #2024_09_04_Time_2_ms_(100.00%)_Space_45.1_MB_(97.99%)
@SuppressWarnings("java:S2234")
public class Solution {
public boolean checkPalindromeFormation(String a, String b) {
- return check(a, b) || check(b, a);
- }
-
- private boolean check(String a, String b) {
- int i = 0;
- int j = b.length() - 1;
- while (j > i && a.charAt(i) == b.charAt(j)) {
- ++i;
- --j;
+ int n = a.length();
+ int s = 0;
+ int e = n - 1;
+ if (isPalindrome(a, b, s, e, true)) {
+ return true;
+ } else {
+ return isPalindrome(b, a, s, e, true);
}
- return isPalindrome(a, i, j) || isPalindrome(b, i, j);
}
- private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int i, int j) {
- while (j > i && s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {
- ++i;
- --j;
+ private boolean isPalindrome(String a, String b, int s, int e, boolean check) {
+ if (s == e) {
+ return true;
+ }
+ while (s < e) {
+ if (a.charAt(s) != b.charAt(e)) {
+ return check
+ && (isPalindrome(a, a, s, e, false) || isPalindrome(b, b, s, e, false));
+ }
+ s++;
+ e--;
}
- return i >= j;
+ return true;
}
}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..8500375b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers;
+
+// #Easy #Math #2024_09_02_Time_0_ms_(100.00%)_Space_40.5_MB_(100.00%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int generateKey(int num1, int num2, int num3) {
+ int s1 =
+ Math.min(((num1 / 1000) % 10), Math.min(((num2 / 1000) % 10), ((num3 / 1000) % 10)))
+ * 1000;
+ int s2 =
+ Math.min(((num1 / 100) % 10), Math.min(((num2 / 100) % 10), ((num3 / 100) % 10)))
+ * 100;
+ int s3 =
+ Math.min(((num1 / 10) % 10), Math.min(((num2 / 10) % 10), ((num3 / 10) % 10))) * 10;
+ int s4 = Math.min((num1 % 10), Math.min((num2 % 10), (num3 % 10)));
+ return s1 + s2 + s3 + s4;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3b3f6fed1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+3270\. Find the Key of the Numbers
+
+Easy
+
+You are given three **positive** integers `num1`, `num2`, and `num3`.
+
+The `key` of `num1`, `num2`, and `num3` is defined as a four-digit number such that:
+
+* Initially, if any number has **less than** four digits, it is padded with **leading zeros**.
+* The ith digit (`1 <= i <= 4`) of the `key` is generated by taking the **smallest** digit among the ith digits of `num1`, `num2`, and `num3`.
+
+Return the `key` of the three numbers **without** leading zeros (_if any_).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** num1 = 1, num2 = 10, num3 = 1000
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+On padding, `num1` becomes `"0001"`, `num2` becomes `"0010"`, and `num3` remains `"1000"`.
+
+* The 1st digit of the `key` is `min(0, 0, 1)`.
+* The 2nd digit of the `key` is `min(0, 0, 0)`.
+* The 3rd digit of the `key` is `min(0, 1, 0)`.
+* The 4th digit of the `key` is `min(1, 0, 0)`.
+
+Hence, the `key` is `"0000"`, i.e. 0.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** num1 = 987, num2 = 879, num3 = 798
+
+**Output:** 777
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** num1 = 1, num2 = 2, num3 = 3
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= num1, num2, num3 <= 9999`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3271_hash_divided_string/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3271_hash_divided_string/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1bc103cc7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3271_hash_divided_string/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3271_hash_divided_string;
+
+// #Medium #String #Simulation #2024_09_02_Time_2_ms_(100.00%)_Space_44.7_MB_(100.00%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public String stringHash(String s, int k) {
+ var result = new StringBuilder();
+ int i = 0;
+ int sum = 0;
+ while (i < s.length()) {
+ sum += s.charAt(i) - 'a';
+ if ((i + 1) % k == 0) {
+ result.append((char) ('a' + sum % 26));
+ sum = 0;
+ }
+ i++;
+ }
+ return result.toString();
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3271_hash_divided_string/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3271_hash_divided_string/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2eca01647
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3271_hash_divided_string/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+3271\. Hash Divided String
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a string `s` of length `n` and an integer `k`, where `n` is a **multiple** of `k`. Your task is to hash the string `s` into a new string called `result`, which has a length of `n / k`.
+
+First, divide `s` into `n / k` **substrings**, each with a length of `k`. Then, initialize `result` as an **empty** string.
+
+For each **substring** in order from the beginning:
+
+* The **hash value** of a character is the index of that character in the **English alphabet** (e.g., `'a' → 0`, `'b' → 1`, ..., `'z' → 25`).
+* Calculate the _sum_ of all the **hash values** of the characters in the substring.
+* Find the remainder of this sum when divided by 26, which is called `hashedChar`.
+* Identify the character in the English lowercase alphabet that corresponds to `hashedChar`.
+* Append that character to the end of `result`.
+
+Return `result`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abcd", k = 2
+
+**Output:** "bf"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+First substring: `"ab"`, `0 + 1 = 1`, `1 % 26 = 1`, `result[0] = 'b'`.
+
+Second substring: `"cd"`, `2 + 3 = 5`, `5 % 26 = 5`, `result[1] = 'f'`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "mxz", k = 3
+
+**Output:** "i"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The only substring: `"mxz"`, `12 + 23 + 25 = 60`, `60 % 26 = 8`, `result[0] = 'i'`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= k <= 100`
+* `k <= s.length <= 1000`
+* `s.length` is divisible by `k`.
+* `s` consists only of lowercase English letters.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0fa9821ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers;
+
+// #Hard #Hash_Table #Math #Enumeration #Combinatorics
+// #2024_09_02_Time_167_ms_(100.00%)_Space_54.5_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import java.util.ArrayList;
+import java.util.Arrays;
+import java.util.HashMap;
+import java.util.HashSet;
+import java.util.List;
+import java.util.Map;
+import java.util.Set;
+
+public class Solution {
+ private final List palindromes = new ArrayList<>();
+
+ private long factorial(int n) {
+ long res = 1;
+ for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
+ res *= i;
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+
+ private Map countDigits(String s) {
+ Map freq = new HashMap<>();
+ for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
+ freq.put(c, freq.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
+ }
+ return freq;
+ }
+
+ private long calculatePermutations(Map freq, int length) {
+ long totalPermutations = factorial(length);
+ for (int count : freq.values()) {
+ totalPermutations /= factorial(count);
+ }
+ return totalPermutations;
+ }
+
+ private long calculateValidPermutations(String s) {
+ Map freq = countDigits(s);
+ int n = s.length();
+ long totalPermutations = calculatePermutations(freq, n);
+ if (freq.getOrDefault('0', 0) > 0) {
+ freq.put('0', freq.get('0') - 1);
+ long invalidPermutations = calculatePermutations(freq, n - 1);
+ totalPermutations -= invalidPermutations;
+ }
+ return totalPermutations;
+ }
+
+ private void generatePalindromes(
+ int f, int r, int k, int lb, int sum, StringBuilder ans, int[] rem) {
+ if (f > r) {
+ if (sum == 0) {
+ palindromes.add(ans.toString());
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = lb; i <= 9; i++) {
+ ans.setCharAt(f, (char) ('0' + i));
+ ans.setCharAt(r, (char) ('0' + i));
+ int chk = sum;
+ chk = (chk + rem[f] * i) % k;
+ if (f != r) {
+ chk = (chk + rem[r] * i) % k;
+ }
+ generatePalindromes(f + 1, r - 1, k, 0, chk, ans, rem);
+ }
+ }
+
+ private List allKPalindromes(int n, int k) {
+ StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder(n);
+ ans.append("0".repeat(Math.max(0, n)));
+ int[] rem = new int[n];
+ rem[0] = 1;
+ for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
+ rem[i] = (rem[i - 1] * 10) % k;
+ }
+ palindromes.clear();
+ generatePalindromes(0, n - 1, k, 1, 0, ans, rem);
+ return palindromes;
+ }
+
+ public long countGoodIntegers(int n, int k) {
+ List ans = allKPalindromes(n, k);
+ Set st = new HashSet<>();
+ for (String str : ans) {
+ char[] arr = str.toCharArray();
+ Arrays.sort(arr);
+ st.add(new String(arr));
+ }
+ List v = new ArrayList<>(st);
+ long chk = 0;
+ for (String str : v) {
+ long cc = calculateValidPermutations(str);
+ chk += cc;
+ }
+ return chk;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..6c28972f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+3272\. Find the Count of Good Integers
+
+Hard
+
+You are given two **positive** integers `n` and `k`.
+
+An integer `x` is called **k-palindromic** if:
+
+* `x` is a palindrome.
+* `x` is divisible by `k`.
+
+An integer is called **good** if its digits can be _rearranged_ to form a **k-palindromic** integer. For example, for `k = 2`, 2020 can be rearranged to form the _k-palindromic_ integer 2002, whereas 1010 cannot be rearranged to form a _k-palindromic_ integer.
+
+Return the count of **good** integers containing `n` digits.
+
+**Note** that _any_ integer must **not** have leading zeros, **neither** before **nor** after rearrangement. For example, 1010 _cannot_ be rearranged to form 101.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 3, k = 5
+
+**Output:** 27
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+_Some_ of the good integers are:
+
+* 551 because it can be rearranged to form 515.
+* 525 because it is already k-palindromic.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1, k = 4
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The two good integers are 4 and 8.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5, k = 6
+
+**Output:** 2468
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 10`
+* `1 <= k <= 9`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..9e5c1e1e1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Sorting #Greedy #2024_09_04_Time_76_ms_(100.00%)_Space_59.5_MB_(61.02%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+@SuppressWarnings("java:S1210")
+public class Solution {
+ public long minDamage(int pw, int[] damage, int[] health) {
+ long res = 0;
+ long sum = 0;
+ for (int e : damage) {
+ sum += e;
+ }
+ Pair[] pairs = new Pair[damage.length];
+ for (int e = 0; e < damage.length; e++) {
+ pairs[e] = new Pair(damage[e], (health[e] + pw - 1) / pw);
+ }
+ Arrays.sort(pairs);
+ for (Pair pr : pairs) {
+ res += pr.val * sum;
+ sum -= pr.key;
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+
+ static class Pair implements Comparable {
+ int key;
+ int val;
+
+ Pair(int key, int val) {
+ this.key = key;
+ this.val = val;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public int compareTo(Pair p) {
+ return val * p.key - key * p.val;
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..289046f26
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+3273\. Minimum Amount of Damage Dealt to Bob
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an integer `power` and two integer arrays `damage` and `health`, both having length `n`.
+
+Bob has `n` enemies, where enemy `i` will deal Bob `damage[i]` **points** of damage per second while they are _alive_ (i.e. `health[i] > 0`).
+
+Every second, **after** the enemies deal damage to Bob, he chooses **one** of the enemies that is still _alive_ and deals `power` points of damage to them.
+
+Determine the **minimum** total amount of damage points that will be dealt to Bob before **all** `n` enemies are _dead_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** power = 4, damage = [1,2,3,4], health = [4,5,6,8]
+
+**Output:** 39
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Attack enemy 3 in the first two seconds, after which enemy 3 will go down, the number of damage points dealt to Bob is `10 + 10 = 20` points.
+* Attack enemy 2 in the next two seconds, after which enemy 2 will go down, the number of damage points dealt to Bob is `6 + 6 = 12` points.
+* Attack enemy 0 in the next second, after which enemy 0 will go down, the number of damage points dealt to Bob is `3` points.
+* Attack enemy 1 in the next two seconds, after which enemy 1 will go down, the number of damage points dealt to Bob is `2 + 2 = 4` points.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** power = 1, damage = [1,1,1,1], health = [1,2,3,4]
+
+**Output:** 20
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Attack enemy 0 in the first second, after which enemy 0 will go down, the number of damage points dealt to Bob is `4` points.
+* Attack enemy 1 in the next two seconds, after which enemy 1 will go down, the number of damage points dealt to Bob is `3 + 3 = 6` points.
+* Attack enemy 2 in the next three seconds, after which enemy 2 will go down, the number of damage points dealt to Bob is `2 + 2 + 2 = 6` points.
+* Attack enemy 3 in the next four seconds, after which enemy 3 will go down, the number of damage points dealt to Bob is `1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4` points.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** power = 8, damage = [40], health = [59]
+
+**Output:** 320
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= power <= 104
+* 1 <= n == damage.length == health.length <= 105
+* 1 <= damage[i], health[i] <= 104
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d511ff87b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color;
+
+// #Easy #String #Math #2024_09_02_Time_0_ms_(100.00%)_Space_41.8_MB_(100.00%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public boolean checkTwoChessboards(String c1, String c2) {
+ int s1 = (c1.charAt(0) - 'a') + (c1.charAt(1) - '0');
+ int s2 = (c2.charAt(0) - 'a') + (c2.charAt(1) - '0');
+ return s1 % 2 == s2 % 2;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..99ca3599f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+3274\. Check if Two Chessboard Squares Have the Same Color
+
+Easy
+
+You are given two strings, `coordinate1` and `coordinate2`, representing the coordinates of a square on an `8 x 8` chessboard.
+
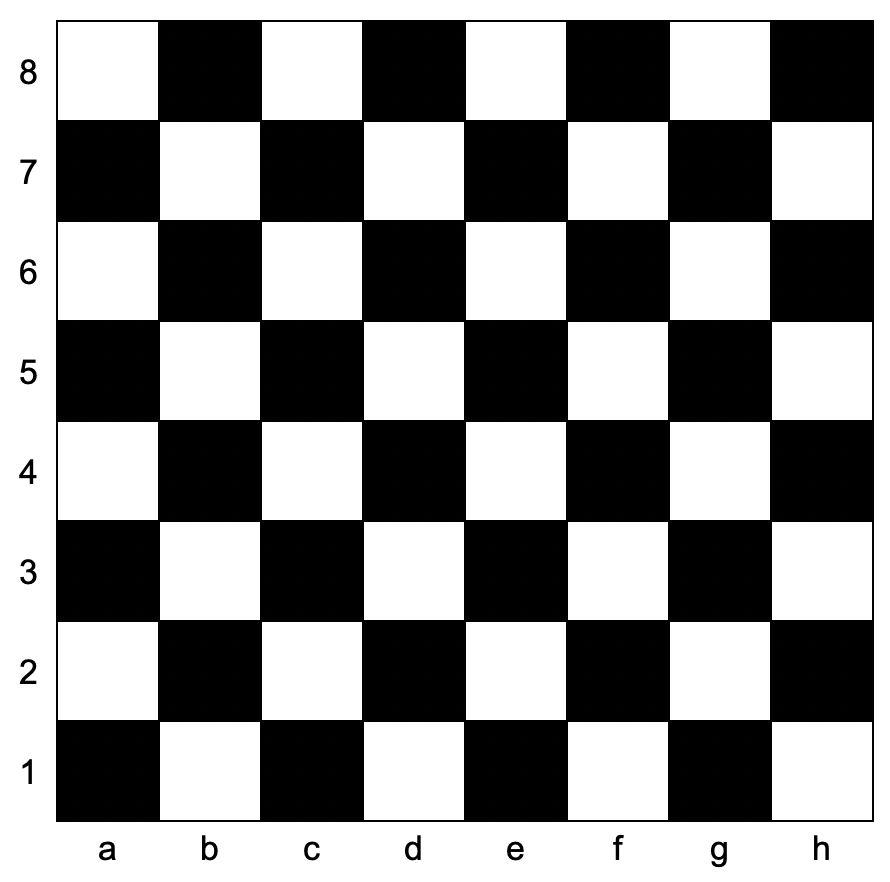
+Below is the chessboard for reference.
+
+
+
+Return `true` if these two squares have the same color and `false` otherwise.
+
+The coordinate will always represent a valid chessboard square. The coordinate will always have the letter first (indicating its column), and the number second (indicating its row).
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** coordinate1 = "a1", coordinate2 = "c3"
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Both squares are black.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** coordinate1 = "a1", coordinate2 = "h3"
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Square `"a1"` is black and `"h3"` is white.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `coordinate1.length == coordinate2.length == 2`
+* `'a' <= coordinate1[0], coordinate2[0] <= 'h'`
+* `'1' <= coordinate1[1], coordinate2[1] <= '8'`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4e88b7445
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Heap_Priority_Queue #2024_09_04_Time_33_ms_(100.00%)_Space_162_MB_(37.19%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int[] resultsArray(int[][] queries, int k) {
+ final int len = queries.length;
+ int[] results = new int[len];
+ int[] heap = new int[k];
+ for (int i = 0; i < k && i < len; i++) {
+ int[] query = queries[i];
+ heap[i] = Math.abs(query[0]) + Math.abs(query[1]);
+ results[i] = -1;
+ }
+ if (k <= len) {
+ buildMaxHeap(heap, k);
+ results[k - 1] = heap[0];
+ }
+ for (int i = k; i < len; i++) {
+ int[] query = queries[i];
+ int dist = Math.abs(query[0]) + Math.abs(query[1]);
+ if (dist < heap[0]) {
+ heap[0] = dist;
+ heapify(heap, 0, k);
+ }
+ results[i] = heap[0];
+ }
+ return results;
+ }
+
+ private void buildMaxHeap(int[] heap, int size) {
+ for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
+ heapify(heap, i, size);
+ }
+ }
+
+ private void heapify(int[] heap, int index, int size) {
+ int root = heap[index];
+ final int left = 2 * index + 1;
+ final int right = 2 * index + 2;
+ if (right < size && root < heap[right] && heap[left] < heap[right]) {
+ heap[index] = heap[right];
+ heap[right] = root;
+ heapify(heap, right, size);
+ } else if (left < size && root < heap[left]) {
+ heap[index] = heap[left];
+ heap[left] = root;
+ heapify(heap, left, size);
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..7842a92a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+3275\. K-th Nearest Obstacle Queries
+
+Medium
+
+There is an infinite 2D plane.
+
+You are given a positive integer `k`. You are also given a 2D array `queries`, which contains the following queries:
+
+* `queries[i] = [x, y]`: Build an obstacle at coordinate `(x, y)` in the plane. It is guaranteed that there is **no** obstacle at this coordinate when this query is made.
+
+After each query, you need to find the **distance** of the kth **nearest** obstacle from the origin.
+
+Return an integer array `results` where `results[i]` denotes the kth nearest obstacle after query `i`, or `results[i] == -1` if there are less than `k` obstacles.
+
+**Note** that initially there are **no** obstacles anywhere.
+
+The **distance** of an obstacle at coordinate `(x, y)` from the origin is given by `|x| + |y|`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** queries = [[1,2],[3,4],[2,3],[-3,0]], k = 2
+
+**Output:** [-1,7,5,3]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Initially, there are 0 obstacles.
+* After `queries[0]`, there are less than 2 obstacles.
+* After `queries[1]`, there are obstacles at distances 3 and 7.
+* After `queries[2]`, there are obstacles at distances 3, 5, and 7.
+* After `queries[3]`, there are obstacles at distances 3, 3, 5, and 7.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** queries = [[5,5],[4,4],[3,3]], k = 1
+
+**Output:** [10,8,6]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* After `queries[0]`, there is an obstacle at distance 10.
+* After `queries[1]`, there are obstacles at distances 8 and 10.
+* After `queries[2]`, there are obstacles at distances 6, 8, and 10.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= queries.length <= 2 * 105
+* All `queries[i]` are unique.
+* -109 <= queries[i][0], queries[i][1] <= 109
+* 1 <= k <= 105
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..84a177bf9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Matrix #Bit_Manipulation #Bitmask
+// #2024_09_04_Time_6_ms_(99.82%)_Space_44.1_MB_(91.67%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+import java.util.List;
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int maxScore(List> grid) {
+ int n = grid.size();
+ int m = grid.get(0).size();
+ int[][] arr = new int[n * m][2];
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ List l = grid.get(i);
+ for (int j = 0; j < l.size(); j++) {
+ arr[i * m + j][0] = l.get(j);
+ arr[i * m + j][1] = i;
+ }
+ }
+ Arrays.sort(arr, (a, b) -> b[0] - a[0]);
+ int[] dp = new int[1 << n];
+ int i = 0;
+ while (i < arr.length) {
+ boolean[] seen = new boolean[n];
+ seen[arr[i][1]] = true;
+ int v = arr[i][0];
+ i++;
+ while (i < arr.length && arr[i][0] == v) {
+ seen[arr[i][1]] = true;
+ i++;
+ }
+ int[] next = Arrays.copyOf(dp, dp.length);
+ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
+ if (seen[j]) {
+ int and = ((1 << n) - 1) ^ (1 << j);
+ for (int k = and; k > 0; k = (k - 1) & and) {
+ next[k | (1 << j)] = Math.max(next[k | (1 << j)], dp[k] + v);
+ }
+ next[1 << j] = Math.max(next[1 << j], v);
+ }
+ }
+ dp = next;
+ }
+ return dp[dp.length - 1];
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3310e3858
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+3276\. Select Cells in Grid With Maximum Score
+
+Hard
+
+You are given a 2D matrix `grid` consisting of positive integers.
+
+You have to select _one or more_ cells from the matrix such that the following conditions are satisfied:
+
+* No two selected cells are in the **same** row of the matrix.
+* The values in the set of selected cells are **unique**.
+
+Your score will be the **sum** of the values of the selected cells.
+
+Return the **maximum** score you can achieve.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,2,3],[4,3,2],[1,1,1]]
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+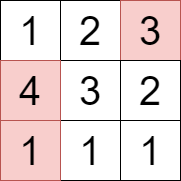
+
+We can select the cells with values 1, 3, and 4 that are colored above.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[8,7,6],[8,3,2]]
+
+**Output:** 15
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+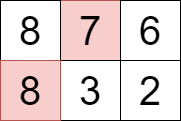
+
+We can select the cells with values 7 and 8 that are colored above.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= grid.length, grid[i].length <= 10`
+* `1 <= grid[i][j] <= 100`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b36b8a47c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #2024_09_04_Time_29_ms_(98.87%)_Space_104.3_MB_(65.54%)
+
+@SuppressWarnings("java:S3012")
+public class Solution {
+ public int[] maximumSubarrayXor(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {
+ int n = nums.length;
+ int[][] dp = new int[n][n];
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ dp[i][i] = nums[i];
+ }
+ for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] ^ dp[i + 1][j];
+ }
+ }
+ for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
+ dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], Math.max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i + 1][j]));
+ }
+ }
+ int q = queries.length;
+ int[] ans = new int[q];
+ int time = 0;
+ for (int[] query : queries) {
+ ans[time++] = dp[query[0]][query[1]];
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..3da27c01e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+3277\. Maximum XOR Score Subarray Queries
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an array `nums` of `n` integers, and a 2D integer array `queries` of size `q`, where queries[i] = [li, ri].
+
+For each query, you must find the **maximum XOR score** of any subarray of nums[li..ri].
+
+The **XOR score** of an array `a` is found by repeatedly applying the following operations on `a` so that only one element remains, that is the **score**:
+
+* Simultaneously replace `a[i]` with `a[i] XOR a[i + 1]` for all indices `i` except the last one.
+* Remove the last element of `a`.
+
+Return an array `answer` of size `q` where `answer[i]` is the answer to query `i`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,8,4,32,16,1], queries = [[0,2],[1,4],[0,5]]
+
+**Output:** [12,60,60]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+In the first query, `nums[0..2]` has 6 subarrays `[2]`, `[8]`, `[4]`, `[2, 8]`, `[8, 4]`, and `[2, 8, 4]` each with a respective XOR score of 2, 8, 4, 10, 12, and 6. The answer for the query is 12, the largest of all XOR scores.
+
+In the second query, the subarray of `nums[1..4]` with the largest XOR score is `nums[1..4]` with a score of 60.
+
+In the third query, the subarray of `nums[0..5]` with the largest XOR score is `nums[1..4]` with a score of 60.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,7,3,2,8,5,1], queries = [[0,3],[1,5],[2,4],[2,6],[5,6]]
+
+**Output:** [7,14,11,14,5]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+| Index | nums[li..ri] | Maximum XOR Score Subarray | Maximum Subarray XOR Score |
+|-------|-----------------------------------|----------------------------|-----------------------------|
+| 0 | [0, 7, 3, 2] | [7] | 7 |
+| 1 | [7, 3, 2, 8, 5] | [7, 3, 2, 8] | 14 |
+| 2 | [3, 2, 8] | [3, 2, 8] | 11 |
+| 3 | [3, 2, 8, 5, 1] | [2, 8, 5, 1] | 14 |
+| 4 | [5, 1] | [5] | 5 |
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n == nums.length <= 2000`
+* 0 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
+* 1 <= q == queries.length <= 105
+* `queries[i].length == 2`
+* queries[i] = [li, ri]
+* 0 <= li <= ri <= n - 1
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..608178227
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3270_find_the_key_of_the_numbers;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void generateKey() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().generateKey(1, 10, 1000), equalTo(0));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void generateKey2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().generateKey(987, 879, 798), equalTo(777));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void generateKey3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().generateKey(1, 2, 3), equalTo(1));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3271_hash_divided_string/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3271_hash_divided_string/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2c0978683
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3271_hash_divided_string/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3271_hash_divided_string;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void stringHash() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().stringHash("abcd", 2), equalTo("bf"));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void stringHash2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().stringHash("mxz", 3), equalTo("i"));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..39db7bfa8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3272_find_the_count_of_good_integers;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void countGoodIntegers() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().countGoodIntegers(3, 5), equalTo(27L));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void countGoodIntegers2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().countGoodIntegers(1, 4), equalTo(2L));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void countGoodIntegers3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().countGoodIntegers(5, 6), equalTo(2468L));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..812d8b433
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3273_minimum_amount_of_damage_dealt_to_bob;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void minDamage() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().minDamage(4, new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4}, new int[] {4, 5, 6, 8}),
+ equalTo(39L));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minDamage2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().minDamage(1, new int[] {1, 1, 1, 1}, new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4}),
+ equalTo(20L));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minDamage3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().minDamage(8, new int[] {40}, new int[] {59}), equalTo(320L));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b5c88aeaf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3274_check_if_two_chessboard_squares_have_the_same_color;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void checkTwoChessboards() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().checkTwoChessboards("a1", "c3"), equalTo(true));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void checkTwoChessboards2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().checkTwoChessboards("a1", "h3"), equalTo(false));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..38fa61c4b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3275_k_th_nearest_obstacle_queries;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void resultsArray() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().resultsArray(new int[][] {{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {2, 3}, {-3, 0}}, 2),
+ equalTo(new int[] {-1, 7, 5, 3}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void resultsArray2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().resultsArray(new int[][] {{5, 5}, {4, 4}, {3, 3}}, 1),
+ equalTo(new int[] {10, 8, 6}));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4ea7ffcac
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3276_select_cells_in_grid_with_maximum_score;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import com_github_leetcode.ArrayUtils;
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void maxScore() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .maxScore(
+ ArrayUtils.getLists(new int[][] {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 3, 2}, {1, 1, 1}})),
+ equalTo(8));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void maxScore2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().maxScore(ArrayUtils.getLists(new int[][] {{8, 7, 6}, {8, 3, 2}})),
+ equalTo(15));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..7af33662b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3277_maximum_xor_score_subarray_queries;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void maximumSubarrayXor() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .maximumSubarrayXor(
+ new int[] {2, 8, 4, 32, 16, 1},
+ new int[][] {{0, 2}, {1, 4}, {0, 5}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {12, 60, 60}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void maximumSubarrayXor2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .maximumSubarrayXor(
+ new int[] {0, 7, 3, 2, 8, 5, 1},
+ new int[][] {{0, 3}, {1, 5}, {2, 4}, {2, 6}, {5, 6}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {7, 14, 11, 14, 5}));
+ }
+}