The features of scheduler are as below:
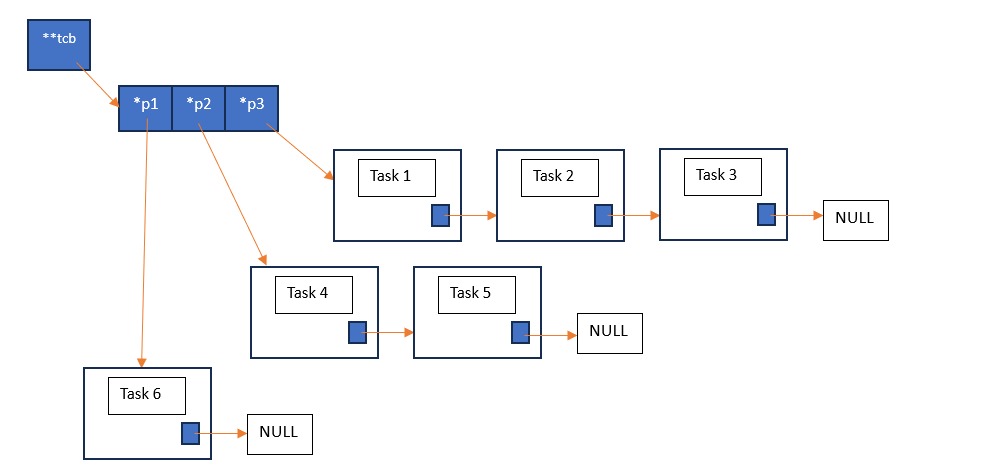
- It features a priority array, which consists of pointers to linked lists of tasks.
- The tasks are represented with help of struct blocks containing parameters such as task name, state, priority, execution time.
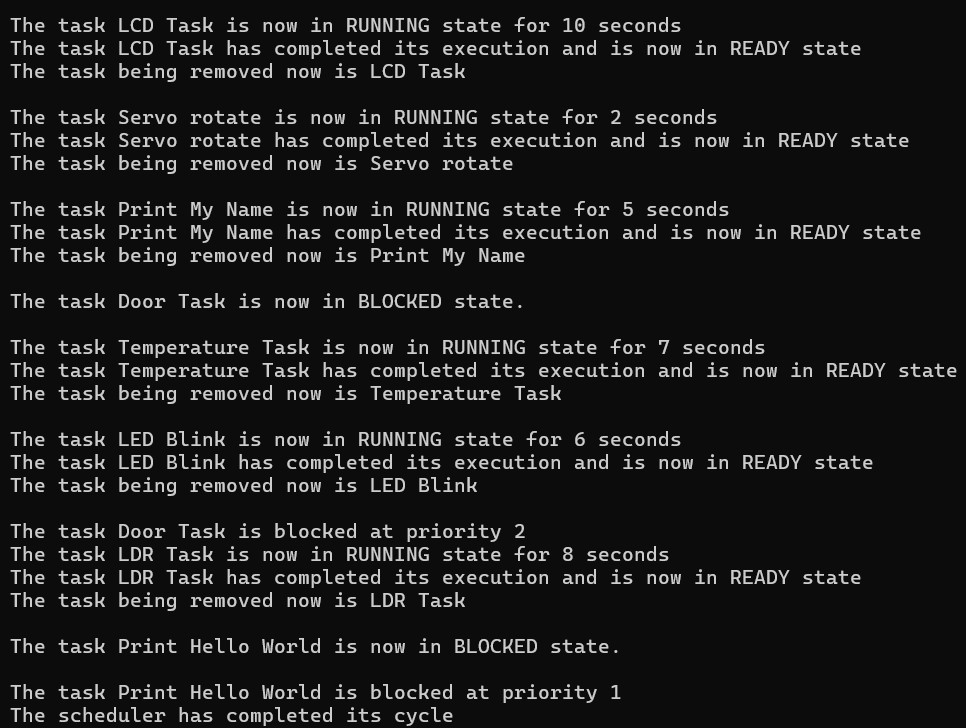
- For each task, there can be three states possible - READY, RUNNING and BLOCKED.
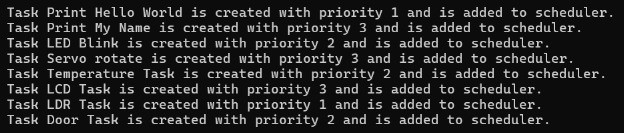
- When a task is created at a particular priority, it is inserted at the head of the linked list at that priority.
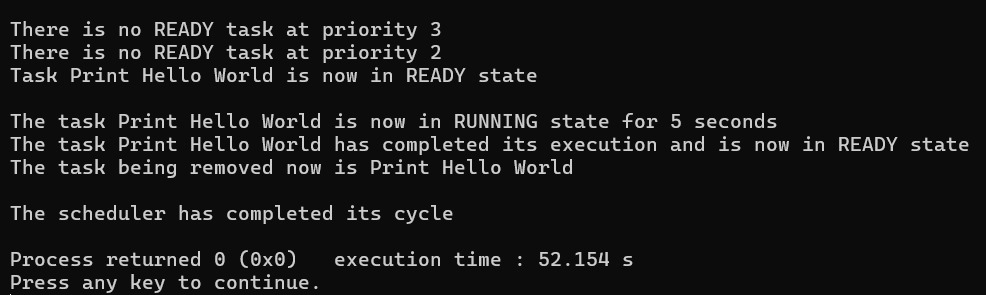
- The scheduler runs in a while(1) loop and breaks if there is no task left at any priority, in any state.
- The scheduler starts executing tasks from the highest priority with the head of the list to be executed first.
- The task execution is simulated simply by using delays equal to the task execution time, created using the sleep() function.
- Once executed, the task is removed from the list and head of the list now points to the task next to the one which just executed.
- Every fourth task that arrives for execution, gets into blocked state.
- A pointer variable keeps track of blocked task and the current task pointer moves to the next task.
- A variable "blockedCount" keeps record of how many times a blocked task is revisited.
- When it is equal to 2 the task's state changes to READY and gets executed.
- A scheduler is said to complete its cycle when it executes all the READY tasks and revisits the BLOCKED tasks in next cycle.