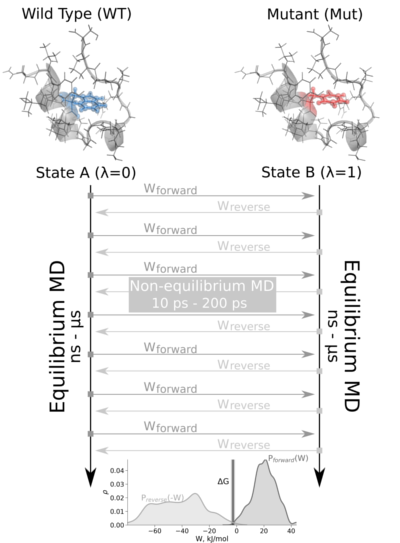
Based on the official pmx tutorial.
This tutorial aims to illustrate how to compute a fast-growth mutation free energy calculation, step by step, using the BioExcel Building Blocks library (biobb). The particular example used is the Staphylococcal nuclease protein (PDB code 1STN), a small, minimal protein, appropriate for a short tutorial.
The non-equilibrium free energy calculation protocol performs a fast alchemical transition in the direction WT->Mut and back Mut->WT. The two equilibrium trajectories needed for the tutorial, one for Wild Type (WT) and another for the Mutated (Mut) protein (Isoleucine 10 to Alanine -I10A-), have already been generated and are included in this example. We will name WT as stateA and Mut as stateB.
The tutorial calculates the free energy difference in the folded state of a protein. Starting from two 1ns-length independent equilibrium simulations (WT and mutant), snapshots are selected to start fast (50ps) transitions driving the system in the forward (WT to mutant) and reverse (mutant to WT) directions, and the work values required to perform these transitions are collected. With these values, Crooks Gaussian Intersection (CGI), Bennett Acceptance Ratio (BAR) and Jarzynski estimator methods are used to calculate the free energy difference between the two states.
Please note that for the sake of disk space this tutorial is using 1ns-length equilibrium trajectories, whereas in the original example the equilibrium trajectories used were obtained from 10ns-length simulations.
- biobb_pmx: Tools to setup and run Alchemical Free Energy calculations.
- biobb_gromacs: Tools to setup and run Molecular Dynamics simulations.
- biobb_analysis: Tools to analyse Molecular Dynamics trajectories.
- jupyter: Free software, open standards, and web services for interactive computing across all programming languages.
- plotly: Python interactive graphing library integrated in Jupyter notebooks.
git clone https://github.com/bioexcel/biobb_wf_pmx_tutorial.git
cd biobb_wf_pmx_tutorial
conda env create -f conda_env/environment.yml
conda activate biobb_wf_pmx_tutorial
jupyter-notebook biobb_wf_pmx_tutorial/notebooks/biobb_wf_pmx_tutorial.ipynbClick here to view tutorial in Read the Docs
Click here to execute tutorial in Binder
Click here to open tutorial in Google Colab
2024.1
This software has been developed in the MMB group at the BSC & IRB for the European BioExcel, funded by the European Commission (EU H2020 823830, EU H2020 675728).
- (c) 2015-2024 Barcelona Supercomputing Center
- (c) 2015-2024 Institute for Research in Biomedicine
Licensed under the Apache License 2.0, see the file LICENSE for details.