-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 77
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
1 parent
551fd56
commit 7a682c9
Showing
4 changed files
with
125 additions
and
6 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1 +1,120 @@ | ||
| # 06-Spinlock -- RISC-V 的嵌入式作業系統 | ||
|
|
||
| ## Spinlock 介紹 | ||
|
|
||
| Spinlock 中文稱做自旋鎖,透過名稱我們就能大概大概猜到 Spinlock 的功用。與 Mutex 相同, Spinlock 可以用來保護 Critical section ,如果執行緒沒有獲取鎖,則會進入迴圈直到獲得上鎖的資格,因此叫做自旋鎖。 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 原子操作 | ||
|
|
||
| 原子操作可以確保一個操作在完成前不會被其他操作打斷,以 RISC-V 為例,它提供了 RV32A Instruction set ,該指令集都是原子操作 (Atomic)。 | ||
|
|
||
| 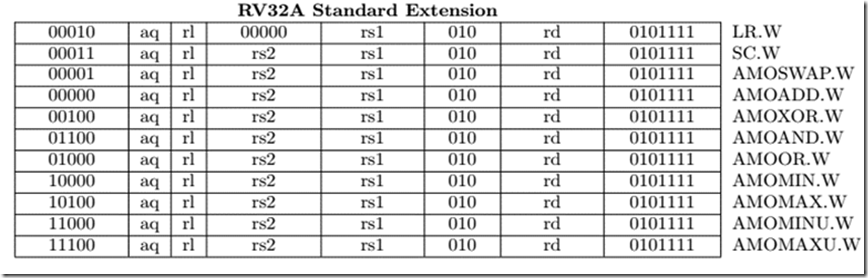 | ||
|
|
||
| 為了避免在同時間有多個 Spinlock 對相同的記憶體做存取,在 Spinlock 實現上會使用到原子操作以確保正確上鎖。 | ||
| > 其實不單單是 Spinlock ,互斥鎖在實現上同樣需要 Atomic operation 。 | ||
| ### 用 C 語言打造簡單的 Spinlock | ||
| 考慮以下程式碼: | ||
| ```c= | ||
| typedef struct spinlock{ | ||
| volatile uint lock; | ||
| } spinlock_t; | ||
| void lock(spinlock_t *lock){ | ||
| while(xchg(lock−>lock, 1) != 0); | ||
| } | ||
| void unlock(spinlock_t *lock){ | ||
| lock->lock = 0; | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
| 透過範例程式碼,可以注意到幾點: | ||
| - lock 的 `volatile` 關鍵字 | ||
| 使用 `volatile` 關鍵字會讓編譯器知道該變數可能會在不可預期的情況下被存取,所以不要將該變數的指令做優化以避免將結果存在 Register 中,而是直接寫進記憶體。 | ||
| - lock 函式 | ||
| [`xchg(a,b)`](https://zh.m.wikibooks.org/zh-hant/X86%E7%B5%84%E5%90%88%E8%AA%9E%E8%A8%80/%E5%9F%BA%E6%9C%AC%E6%8C%87%E4%BB%A4%E9%9B%86/IA32%E6%8C%87%E4%BB%A4:xchg) 可以將 a, b 兩個變數的內容對調,並且該函式為原子操作,當 lock 值不為 0 時,執行緒便會不停的自旋等待,直到 lock 為 0 (也就是可供上鎖)為止。 | ||
| - unlock 函式 | ||
| 由於同時間只會有一個執行緒獲得鎖,所以在解鎖時不怕會有搶占存取的問題。也因為這樣,範例就沒有使用原子操作了。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## mini-riscv-os 中的自旋鎖 | ||
|
|
||
| ### basic lock | ||
|
|
||
| 首先,由於 mini-riscv-os 是屬於 Single hart 的作業系統,除了使用原子操作以外,其實還有一個非常簡單的作法可以做到 Lock 的效果: | ||
| ```c= | ||
| void basic_lock() | ||
| { | ||
| w_mstatus(r_mstatus() & ~MSTATUS_MIE); | ||
| } | ||
| void basic_unlock() | ||
| { | ||
| w_mstatus(r_mstatus() | MSTATUS_MIE); | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
| 在 [lock.c] 中,我們實作了非常簡單的鎖,當我們在程式中呼叫 `basic_lock()` 時,系統的 machine mode 中斷機制會被關閉,如此一來,我們就可以確保不會有其他程式存取到 Shared memory ,避免了 Race condition 的發生。 | ||
|
|
||
| ### spinlock | ||
|
|
||
| 上面的 lock 有一個明顯的缺陷: **當獲取鎖的程式一直沒有釋放鎖,整個系統都會被 Block** ,為了確保作業系統還是能維持多工的機制,我們勢必要實作更複雜的鎖: | ||
| - [os.h] | ||
| - [lock.c] | ||
| - [sys.s] | ||
|
|
||
| ```c= | ||
| typedef struct lock | ||
| { | ||
| volatile int locked; | ||
| } lock_t; | ||
| void lock_init(lock_t *lock) | ||
| { | ||
| lock->locked = 0; | ||
| } | ||
| void lock_acquire(lock_t *lock) | ||
| { | ||
| for (;;) | ||
| { | ||
| if (!atomic_swap(lock)) | ||
| { | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| void lock_free(lock_t *lock) | ||
| { | ||
| lock->locked = 0; | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 其實上面的程式碼與前面介紹 Spinlock 的範例基本上一致,我們在系統中實作時只需要處理一個比較麻煩的問題,也就是實現原子性的交換動作 `atomic_swap()`: | ||
| ```assembly= | ||
| .globl atomic_swap | ||
| .align 4 | ||
| atomic_swap: | ||
| li a5, 1 | ||
| amoswap.w.aq a5, a5, 0(a0) | ||
| mv a0, a5 | ||
| ret | ||
| ``` | ||
| 在上面的程式中,我們將 lock 結構中的 locked 讀入,與數值 `1` 做交換,最後再回傳暫存器 `a5` 的內容。 | ||
| 進一步歸納程式的執行結果,我們可以得出兩個 Case: | ||
| 1. 成功獲取鎖 | ||
| 當 `lock->locked` 為 `0` 時,經過 `amoswap.w.aq` 進行交換以後, `lock->locked` 值為 `1` ,回傳值 (Value of a5) 為 `0`: | ||
| ```c= | ||
| void lock_acquire(lock_t *lock) | ||
| { | ||
| for (;;) | ||
| { | ||
| if (!atomic_swap(lock)) | ||
| { | ||
| break; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
| 當回傳值為 `0` , `lock_acquire()` 就會順利跳出無窮迴圈,進入到 Critical sections 執行。 | ||
| 2. 沒有獲取鎖 | ||
| 反之,則繼續在無窮迴圈中嘗試獲得鎖。 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 延伸閱讀 | ||
| 如果對 `Race Condition` 、 `Critical sections` 、 `Mutex` 有興趣,可以閱讀 [AwesomeCS Wiki](https://github.com/ianchen0119/AwesomeCS/wiki) 中的並行程式設計一節。 |