-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2.8k
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Louis1992
committed
Jun 23, 2015
1 parent
4aae037
commit b8046d1
Showing
22 changed files
with
551 additions
and
97 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,56 @@ | ||
| ### Exercises 6.1-1 | ||
| *** | ||
| What are the minimum and maximum numbers of elements in a heap of height h? | ||
|
|
||
| ### `Answer` | ||
| 最多就是一颗很完美的二叉树,是2\*\*(h+1) − 1 ; 最少的话最后一层只有一个,是2\*\*h | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ### Exercises 6.1-2 | ||
| *** | ||
| Show that an n-element heap has height ⌞lg n⌟ | ||
|
|
||
| ### `Answer` | ||
| 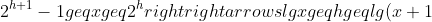-1 ) | ||
|
|
||
| 所以h = ⌞lg n⌟ | ||
|
|
||
| ### Exercises 6.1-3 | ||
| *** | ||
| Show that in any subtree of a max-heap, the root of the subtree contains the largest value occurring anywhere in that subtree. | ||
|
|
||
| ### `Answer` | ||
| 这就是最大堆的性质. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Exercises 6.1-4 | ||
| *** | ||
| Where in a max-heap might the smallest element reside, assuming that all elements are distinct? | ||
|
|
||
| ### `Answer` | ||
| 肯定是在叶子节点. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Exercises 6.1-5 | ||
| *** | ||
| Is an array that is in sorted order a min-heap? | ||
|
|
||
| ### `Answer` | ||
| 没有说明是递增数组还是递减数组,所以不一定. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Exercises 6.1-6 | ||
| *** | ||
| Is the sequence [23, 17, 14, 6, 13, 10, 1, 5, 7, 12] a max-heap? | ||
|
|
||
| ### `Answer` | ||
| 不是,7 > 6 | ||
|
|
||
| ### Exercises 6.1-7 | ||
| *** | ||
| Show that, with the array representation for storing an n-element heap, the leaves are the nodes indexed by ⌞n/2⌟ + 1, ⌞n/2⌟ + 2, ... , n. | ||
|
|
||
| ### `Answer` | ||
| 挺容易推的,因为每增加两个节点,树的叶子节点就会往后推移一位.再注意一下取整的位置就行. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| *** | ||
| Follow [@louis1992](https://github.com/gzc) on github to help finish this task. | ||
|
|
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,64 @@ | ||
| /************************************************************************* | ||
| > File Name: d-ary-heaps.cpp | ||
| > Author: Louis1992 | ||
| > Mail: [email protected] | ||
| > Blog: http://gzc.github.io | ||
| > Created Time: Tue Jun 23 19:22:21 2015 | ||
| ************************************************************************/ | ||
| #include<iostream> | ||
| #include<cstdio> | ||
| #include<climits> | ||
| using namespace std; | ||
|
|
||
| #define PARENT(i,d) ((i - 1) / d) | ||
| #define CHILD(i,c,d) (3 * i + c + 1) | ||
|
|
||
| typedef struct { | ||
| int *elements; | ||
| int d; | ||
| int heap_size; | ||
| } heap_t; | ||
|
|
||
| void max_heapify(heap_t *heap, int i) { | ||
| int largest = i; | ||
| int basechild = CHILD(i, 0, heap->d); | ||
|
|
||
| for (int k = 0; k < heap->d; k++) { | ||
| int child = basechild+k; | ||
| if (child < heap->heap_size && heap->elements[child] > heap->elements[largest]) | ||
| largest = child; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| if (largest != i) { | ||
| swap(heap->elements[i],heap->elements[largest]); | ||
| max_heapify(heap, largest); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| int extract_max(heap_t *heap) { | ||
| int max = heap->elements[0]; | ||
| heap->elements[0] = heap->elements[heap->heap_size - 1]; | ||
| heap->heap_size--; | ||
| max_heapify(heap, 0); | ||
| return max; | ||
| }; | ||
|
|
||
| void increase_key(heap_t *heap, int i, int key) { | ||
| if (key < heap->elements[i]) { | ||
| cerr << "new key is smaller than current key" << endl; | ||
| exit(-1); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| while (i > 0 && heap->elements[PARENT(i,heap->d)] < key) { | ||
| heap->elements[i] = heap->elements[PARENT(i,heap->d)]; | ||
| i = PARENT(i,heap->d); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| heap->elements[i] = key; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| void insert(heap_t *heap, int key) { | ||
| heap->heap_size++; | ||
| heap->elements[heap->heap_size - 1] = INT_MIN; | ||
| increase_key(heap, heap->heap_size - 1, key); | ||
| } |
File renamed without changes.
File renamed without changes.
File renamed without changes.
File renamed without changes.
File renamed without changes.
Oops, something went wrong.