- 자바 플랫폼을 위한 오픈 소스 애플리케이션 프레임워크
- 스프링 프레임워크의 구성은 20여가지로 구성되어 있다.(https://spring.io/projects/spring-framework)
- 각 모듈들은 스프링의 핵심 기능(DI, AOP, etc) 을 제공해주며, 필요한 모듈만 선택하여 사용 (아래 모듈들에 중점을 둔다)
- Spring Boot : 웹 서버를 올림
- Spring Data : JDBC, JPA ...
- Spring Batch : 대용량 데이터 처리
- Spring Security : 권한 관련
- Spring Cloud
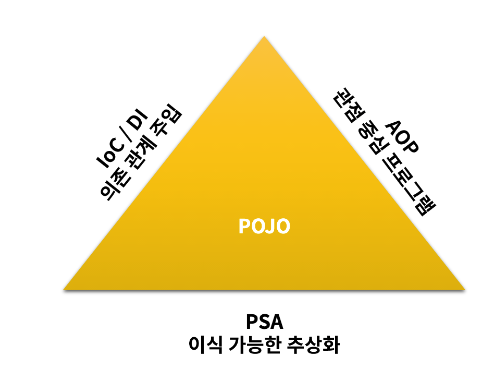
- 스프링은 Spring Triangle(IoC, AOP, PSA) 이라고 부르는 위 세 가지 개념을 제공한다.
- 제어의 역전
- 스프링에서는 일반적인 Java 객체를 new 로 생성하여 개발자가 관리하지 않고 Spring Container 에게 제어의 객체 관리 권한을 모두 맡긴다. (스프링이 알아서 객체의 생명주기를 관리해줌)
- 개발자가 객체를 사용하기 위해서는 외부(스프링 컨테이너)로부터 주입을 받는다. -> DI
- 의존성주입
- 의존성으로부터 격리시켜 코드 테스트에 용이하다.
- 코드를 확장하거나 변경할 때 영향을 최소화 한다.(추상화)
- 순환 참조를 막을 수 있다.
@Component
public class ApplicationContextProvider implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext context;
@Override
// 외부(스프링)으로부터 주입을 받음 -> applicationContext 을 주입 받음
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
context = applicationContext;
}
public static ApplicationContext getContext(){
return context;
}
}IocApplication.java 의 일부
@Configuration
public class AppConfig{
@Bean
public Encoder encoder(Base64Encoder base64Encoder){
return new Encoder(base64Encoder);
}
@Bean
public Encoder encoder(UrlEncoder urlEncoder){
return new Encoder(urlEncoder);
}
}- @Component : 스프링 컨테이너에서 직접 스프링 빈으로 만들어서 관리를 해줌
- @Bean : @Component 와 동일하지만 메서드에만 적용 가능. @Component 는 클래스에 적용 가능.
- 스프링 빈 찾기 : applicationContext.getBean() 메서드 이용
- @Qualifier("beanName") -> 매칭할 Bean 을 지정해줄 수 있음
- @Configuration : 한 개의 클래스에서 여러 Bean 을 등록할 것이라는 의미
- Aspect Oriented Programming 관점 지향 프로그래밍
class A {
method a(){
AAAA
wording method a
BBBB
}
method b(){
AAAA
wording method b
BBBB
}
method c(){
AAAA
wording method c
BBBB
}
}위와 같이 동일한 일을 하는 코드 AAAA, BBBB 가 중복될 때, AOP 는 여러 곳에서 사용되는 중복코드는 떼어서 분리하고 method a, b, c 는 각자 자신이 해야할 작업(aspect)만 가지고 있게 해준다. (ex. 여러 메서드들에서 사용되는 파라미터 로깅, 실행시간 로깅, 파라미터 인코딩 등의 작업을 일괄적으로 처리)
- aop 를 사용하기 위해서는 dependencies 를 추가해주어야 한다.
주요 Annotation
| Annotation | 의미 |
|---|---|
| @Aspect | AOP 를 정의하는 Class 에 할당 |
| @Pointcut | AOP 를 적용시킬 지점을 설정 |
| @Before | 메서드를 실행하기 이전 |
| @After | 메서드가 성공적으로 실행 후, 예외가 발생 되더라도 실행 |
| @AfterReturning | 메서드 호출 성공시 실행 (Not Throws) |
| @AfterThrowing | 메소드 호출 실패시 실행(예외발생 Throws) |
| @Around | Before / After 모두 제어 |
@Aspect
@Component
public class ParameterAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut(){}
// aop.controller 라는 패키지 하위에 있는 모든 메서드를 다 aop 로 보겠다. aop 를 적용시킬 지점은 cut() 메서드.
// cut() 메서드가 실행되는 시점의 before(전) 에 이 메서드를 실행시킨다.
@Before("cut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){ // JoinPoint : 들어가는 지점에 대한 정보를 가지고 있는 객체
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
System.out.println(method.getName());
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for(Object obj : args){
System.out.println("type : "+obj.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("value : "+obj);
}
}
// cut() 메서드가 정상 실행되고 리턴이 되면 아래 메서드를 실행한다. 리턴된 값이 returnObj 로 들어옴.
@AfterReturning(value = "cut()", returning = "returnObj")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnObj){
System.out.println("return obj");
System.out.println(returnObj);
}
}